
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Simply put, robotic process automation, or RPA, is the application of technology to automate rules-based business processes. It has the ability to emulate any repetitive human actions to streamline workflows and increase efficiencies resulting in significant ROI and resource savings. RPA tasks can range from something as simple as data entry to automating the complexities of data extractions for decommissioning systems or migrating EHRs.
RPA acts as a unique temporary or full-time employee to supplement your department or business unit. It gets projects done in a fraction of the time it would take a human, works 24x7x365, and never gets tired. There’s a reason why robotic process automation is seeing its fastest growth across all industries, especially healthcare.
Forrester predicts the RPA software market to total $2.9 billion in the year ahead:
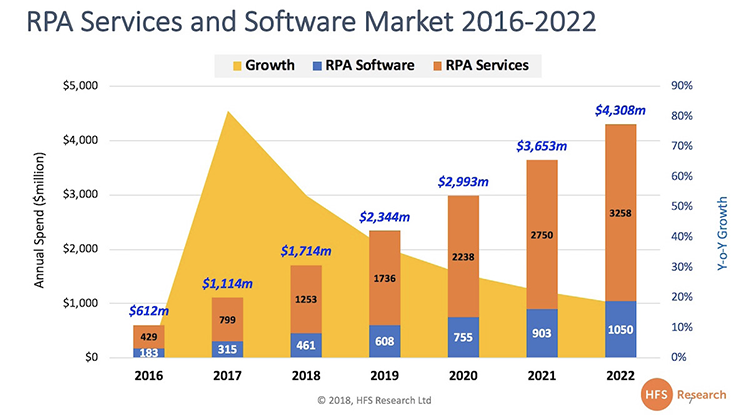
Source: HFS Research
By automating any workflow faster and more accurately than a human user, the ROI is almost immediate. The significant time, cost, and resource savings will enable your organization to remain sustainable and continue to save money over time.
Automation as a Complement to Employees
Robotic process automation isn’t meant to replace positions, but rather assist with fluctuations in workloads and staffing, and allow employees to be reallocated to more rewarding projects. This leads to an improvement in employee satisfaction and alleviates staff burnout.
According to Harvard Business Review, most groups adopting RPA have assured their employees that automation would not result in layoffs. Instead, workers have been redeployed to do more interesting work. One academic study highlighted that workers did not feel threatened by automation: they embraced it and viewed the robots as team-mates. The same study highlighted that, rather than resulting in a lower headcount, the technology was deployed in such a way as to achieve more work and greater productivity with the same number of people.
Larger projects such as EHR migrations, legacy system archiving, end-of-year billing and account reconciliation, etc., would typically require the hiring of additional temporary or full-time equivalents (FTE) due to the anticipated increase in workloads. However, deploying RPA could provide enough support of such projects that the hospital can avoid increasing the headcount, paying for additional hours of overtime, or hiring outside consultants to assist with these efforts. Other one-off projects or even the unanticipated shifting of priorities can also be supplemented with RPA. The industry saw this a lot over the past year. COVID-19 test registration and reporting can be manually intensive and time consuming for hospital staff. By using automation to support these workflows, lab results can arrive faster and more efficiently to both medical and IT systems. By tasking “virtual assistants” with result registration, human employees have more time to deliver critical front-line patient care, a job which will never go extinct.
Overall, completing high volumes of repetitive, monotonous projects leads to burnout and employee dissatisfaction. Having an automation tool to manage any of those daily tasks such as data entry or other administrative duties allows staff to focus on more critical thinking projects associated with the jobs and skills they were hired for, and in many cases prevents staff from having to work a high number of overtime hours, which significantly impacts the budget. Allocating automation to assist with certain functions better-enables employees to focus on the more rewarding aspects of their position. For example, utilizing RPA to produce PDF reports for use in downtime situations will allow clinicians to spend less time printing and sorting hundreds of pages of documents, and more time providing care to the actual patients. There are aspects of every hospital department that could use the added support of RPA to allow staff to be more productive and efficient in their main roles.
Another example involves operating room (OR) management preference cards, which need to be updated ahead of all operations and surgical procedures. Automating a workflow which could run overnight, would save staff hours of time and allow the OR to run more efficiently and safely for the surgeons and patients the following day.
According to a Deloitte RPA Survey, the benefits of RPA adoption are significant. ROI was reported at less than 12 months, with an average 20% of FTE capacity provided by RPA technology. It continues to meet and exceed expectations across multiple dimensions including:
- Improved compliance (92%)
- Improved quality/accuracy (90%)
- Improved productivity (86%)
- Cost reduction (59%)
 Source: Summit Healthcare
Source: Summit Healthcare
Taking a Closer Look
Improved Scalability and Efficiencies
Unlike human users, robotic process automation allows organizations to scale repetitive tasks nearly immediately, which can contribute to increased productivity, time and cost savings, and overall improved productivity. Building a workflow to streamline a process in one part of your organization can be expanded by reusing or creating similar automated workflows for other projects across job functions and even organization-wide.
Improved Quality and Compliance
Automation technology isn’t subject to fatigue or human error. Using emulation within day-to-day operations can help provide a consistent basis of service and care activities. Even the most perfect employee might commit a few human errors, which can be wiped out with RPA. The results of these errors might be significant in the long run. And in the world of healthcare, even a small mistake can cost a life. However, when you are automating a task, you are reducing the chance of the mistake and hence, helping to make the healthcare procedure more effective and efficient. You’re also limiting employee’s contact with protected health information which increases security and protects your organization from compliance issues.
Labor Savings
Using automation to replace manually intensive tasks can be a big time-saver, completing tasks in a fraction of the time it would take an FTE. Free your team from mundane, repetitive, data entry tasks. Instead, elevate your employees to higher-functioning roles that take advantage of expertise they’ve been trained for. Employee morale may improve along with reduced burnout, which is a large factor in employee satisfaction and morale. Robotic process automation can also be used to supplement workload fluctuations due to busy periods, employee vacations, and the increased necessity for working remotely.
Reduced Waste
Most organizations report experiencing an ROI in less than 12 months from implementing an RPA solution. Aside from the obvious time, labor and cost savings, use of paper and spreadsheets and other workarounds needed for an overfull workload can lead to a lot of waste. For example, rather than playing phone tag with a discharged patient in the free minutes between hospital nursing duties, automation can help get nurses and patients connected more efficiently.
The Virtual Employee You Didn’t Know You Needed, Until Now
Think of all the ways you could better allocate your staff, or manage a limited staff, if you have a virtual assistant to help with those tedious, time consuming projects. Additionally, how much are you paying your employees? Hours of busy work cost an organization significantly more than the tasks are actually worth. Think about the hourly pay rate of employees in your organization that do data entry or routine tasks on a regular basis. What would be the tipping point at which it makes sense to automate those ongoing tasks and allow those employees to do more rewarding or critical work?
A simple assessment can help you determine where automation should be applied throughout your organization:
- Do you manage a high volume of rules-based and repetitive tasks?
- Do you run standard reports daily, weekly, hourly, monthly?
- Are there tasks that consume many hours of manual labor?
- Do you have data entry tasks where data is available in a file?
- Are there certain tasks prone to human error?
- Is there other work your employees (or you) should be doing with the time spent doing any of the above?
Approximately 10% to 20% of human work hours are spent on dull, repetitive computer tasks, according to Software Testing and Big Data Hadoop, marking quite a large chunk of time that is wasted on processes that can be easily automated. Researchers at the company estimate that IT departments also spend 30% of their time on low-level basic tasks. Plus, about 50% of companies spend $5 to $25 per manually-processed invoice.
Once thought of as solely an IT tool, robotic process automation can be expanded throughout the hospital or health system to support a multitude of departments and job functions. Have you thought about all of the organizational areas where an intelligent workflow automation assistant could take over?
Accounting/Finance
- Bad debt write offs
- GL code or periodic finance code creation
- Insurance processing
- Payroll processing
- Processing electronic payments
- Tax processes
HR/Payroll
- Employee benefit processing
- Employee credentialing and de-credentialing
- Employee exit procedures
- New hire procedures
- Payroll updates
Medical Records
- Notes processing
- Patient admission and discharge records processing
- Patient records access audit
- Scanned document processing
Information Technology
- Automated interfaces
- Dictionary/Domain updates
- System upgrade testing
- System conversions and migrations
Using RPA to Connect Disparate Systems
The use of robotic process automation has evolved dramatically over the past few years. Automated workflows, or scripted interfaces, were originally used to connect two disparate systems, typically using a spreadsheet or database as a medium. However, they can also provide application connectivity where traditional HL7 interfaces are not an option, or are considered too expensive. An automated workflow is also highly desirable when the connection must be made rapidly to meet a tight deadline, such as for a major EHR upgrade. This is because an interface of this type is quick to deploy and can achieve almost real-time data exchange, as well as providing a means to map or cross-walk data between systems.
For batch, real-time and interactive interfaces, automation is a solid interface method.
Sometimes the best solution is to use a combination of scripting and HL7. If you have a standard HL7 interface that you want to leverage (due to volume of data, etc.), yet need some level of customization for your interface project, an integration partner can often provide the necessary assistance with scripting.
 Source: Summit Healthcare
Source: Summit Healthcare
Conclusion
Now more than ever, hospitals are looking for ways to control rising costs and improve financial stability while maintaining staff levels and providing quality patient care. There has been significant revenue loss from cancelled services due to COVID-19, as well as increased costs due to the need for purchasing PPE and other unprecedented needs. The American Hospital Association estimates a total four-month financial impact of $202.6 billion in losses for America’s hospitals and health systems, or an average of $50.7 billion per month.
RPA cannot account for all cost-savings, but understanding the potential impact of implementing an automation platform across health systems can significantly jump start your bottom line. From conversations with users, most organizations report seeing an ROI in months, if not weeks, after implementing an automation solution. As improvements continue to be made to the technology, and employees are reallocated to play more critical roles in organizations, robotic process automation can fill that gap to allow employees to focus on what really matters.
The views and opinions expressed in this content or by commenters are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of HIMSS or its affiliates.
Clinical & Business Intelligence Community
Clinical and business intelligence is the aggregation, analysis and use of clinical, financial, operational and non-traditional data to inform decision-making. Our Clinical & Business Intelligence Community can help you positively impact care delivery, health outcomes and business operations at your organization, and beyond.



